Reverse osmosis is a process that purifies water by using high pressure to change the osmotic pressure in water. This process is not thermal in nature and doesn’t use any energy. It uses brackish water, which is a bit saltier than fresh water but less salty than seawater. The process uses between 200 and 400 pounds of pressure per square inch (psi) to remove the contaminants. This process can be used to purify up to one gallon of water per hour, and requires a small tank to operate.
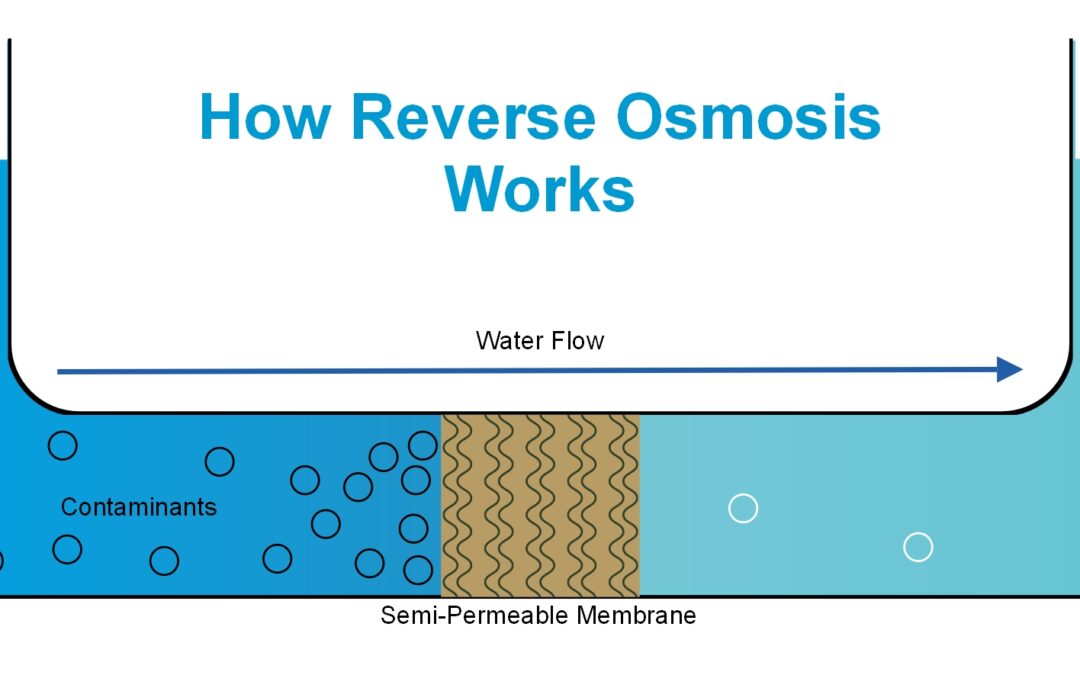
Reverse osmosis is a type of filtration process that removes the majority of contaminants from water. The process involves forcing water through a thin membrane with a very specific pore size. The membrane allows only water molecules to pass through, while the larger contaminant particles are trapped and removed. The result is a pure drinking water. There are several different kinds of reverse osmosis systems.
Reverse osmosis water systems are made up of three to five stages of filtration. The first step is a sediment filter, followed by a carbon filter. The second stage is a postfilter. The prefilter is used to remove contaminants like chlorine, sediment, and dissolved solids. The final step is the reverse osmosis membrane. Reverse osmosis filters also use other types of filtration, including distillation and reverse osmosis.
Another benefit of reverse osmosis water is that the minerals removed during the purification process aren’t harmful to humans. They can be replaced by foods and supplements. Furthermore, drinking reverse osmosis water is a safer alternative to drinking water that has been polluted with pesticides and heavy metals. Intake of polluted water can lead to significant health complications.
Reverse osmosis is an excellent water filtration system. It filters the water by forcing it through a semi-permeable membrane. This semi-permeable membrane removes many contaminants and other materials from water. The process also improves the taste and odor of water.